Applications
Contents
- Intro to SPICE Algorithm
- Framework and your first circuit!
- More Static Linear Components
- Nonlinear and Diode
- MOSFET
- Time Variance
- Applications (this article)
Please obtain my permission before sharing this with others.
ASP notes page
This page is under construction.
Welcome to AP!
This page is under construction.
Fundies ODS Notes
The notes are organized sequentially with the lecture.
Biology video project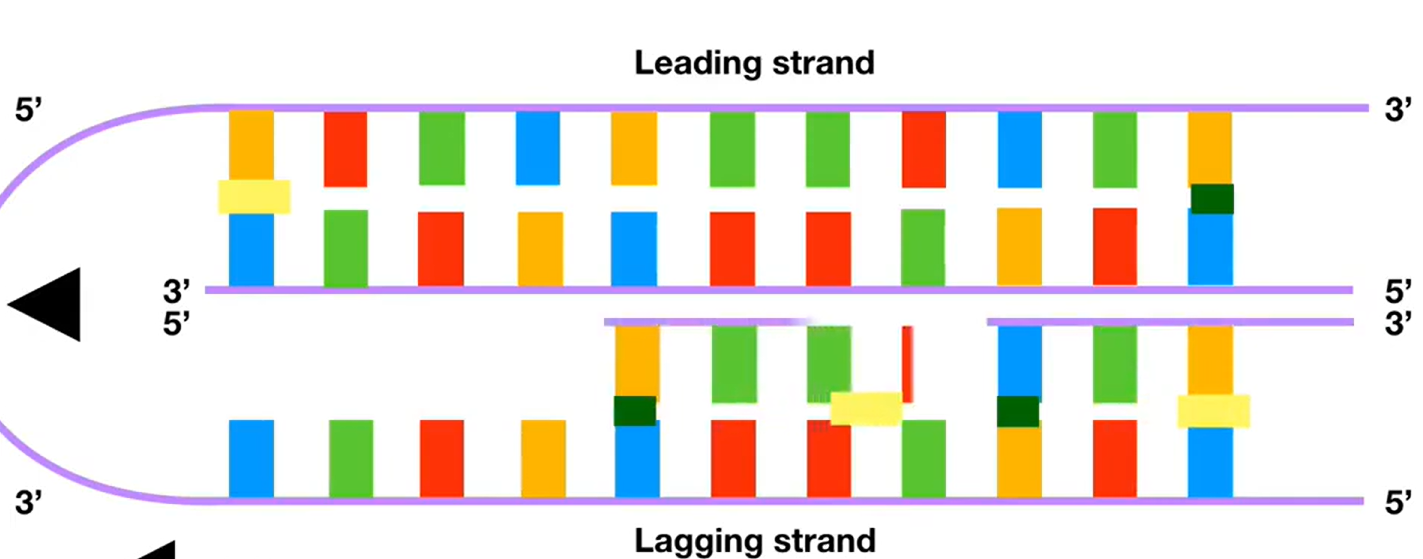
ODE final project 
CST Final Project
SCHUDEM VIII outstanding award winner 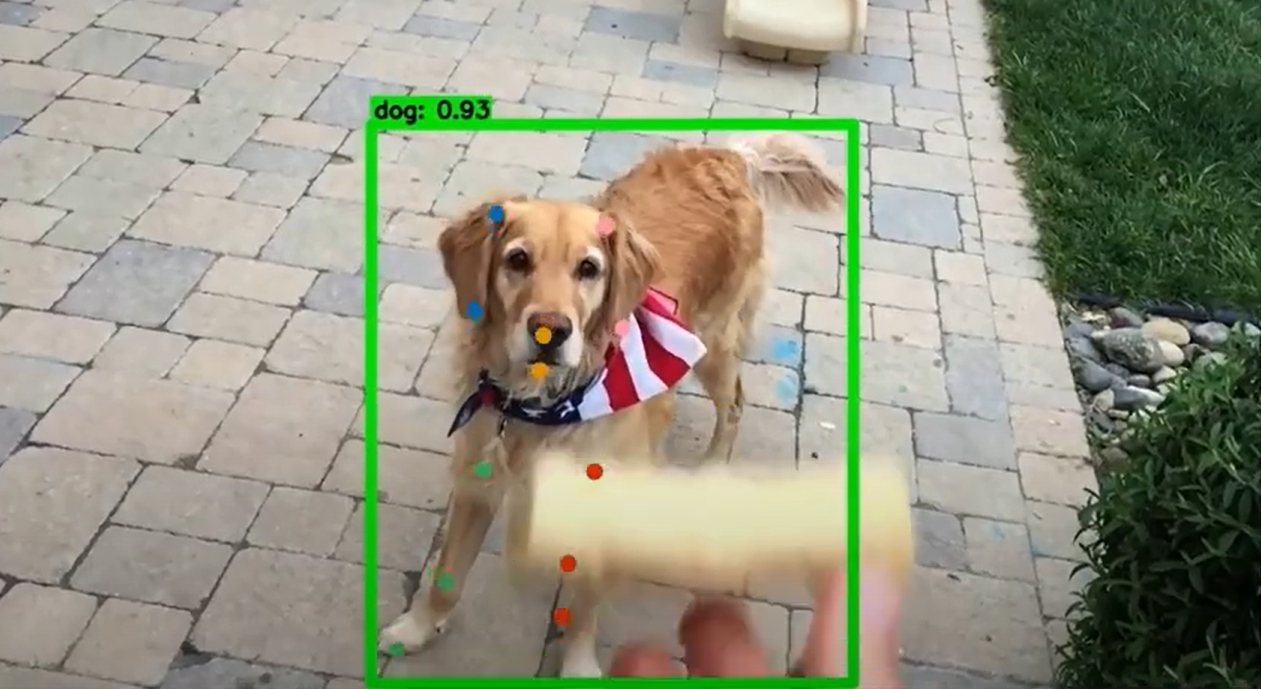
Eco-Literature Final Project 
Final project for MATH 312 Analysis I
Final project for PHYS 221 Relativity and Cosmology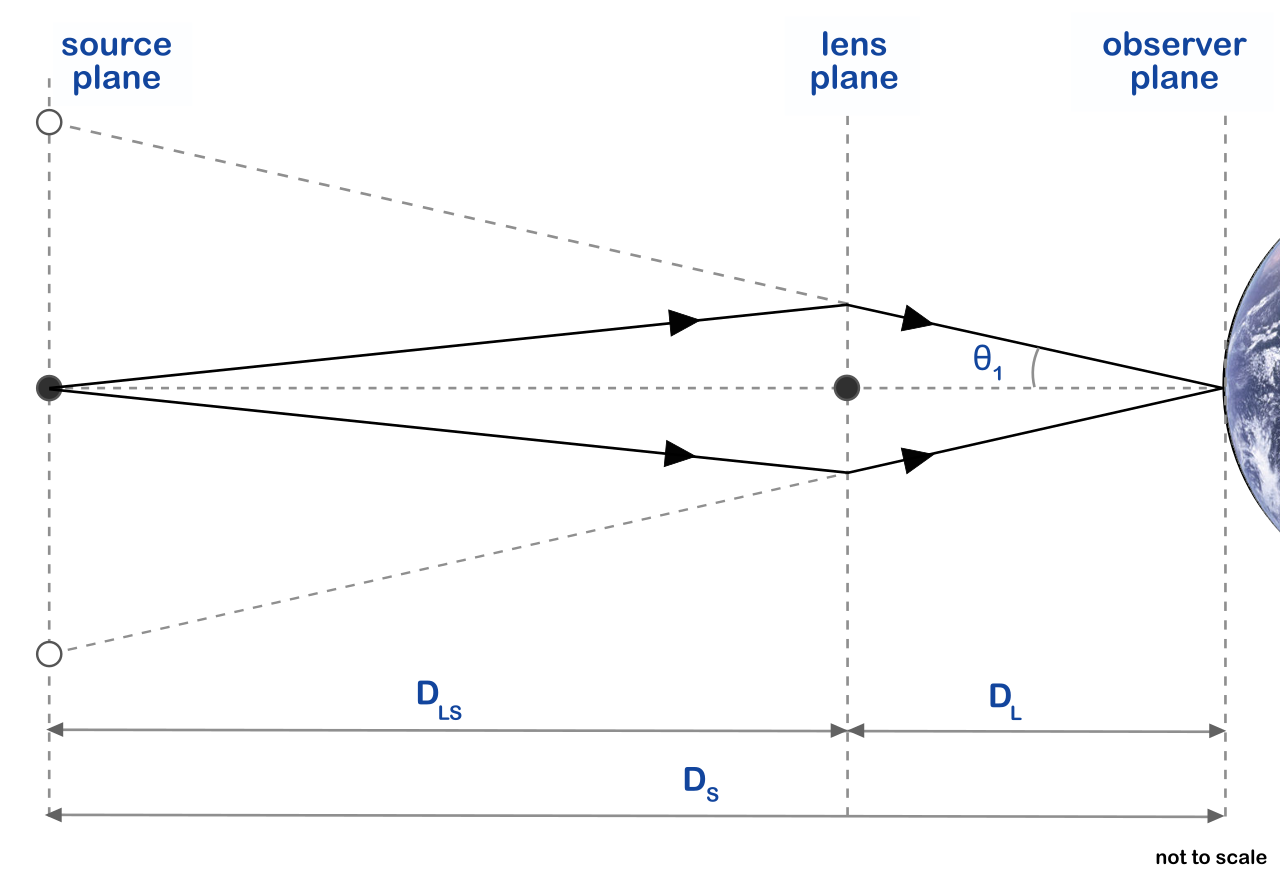
HTTP server/client from scratch
Final Project for Computer Networks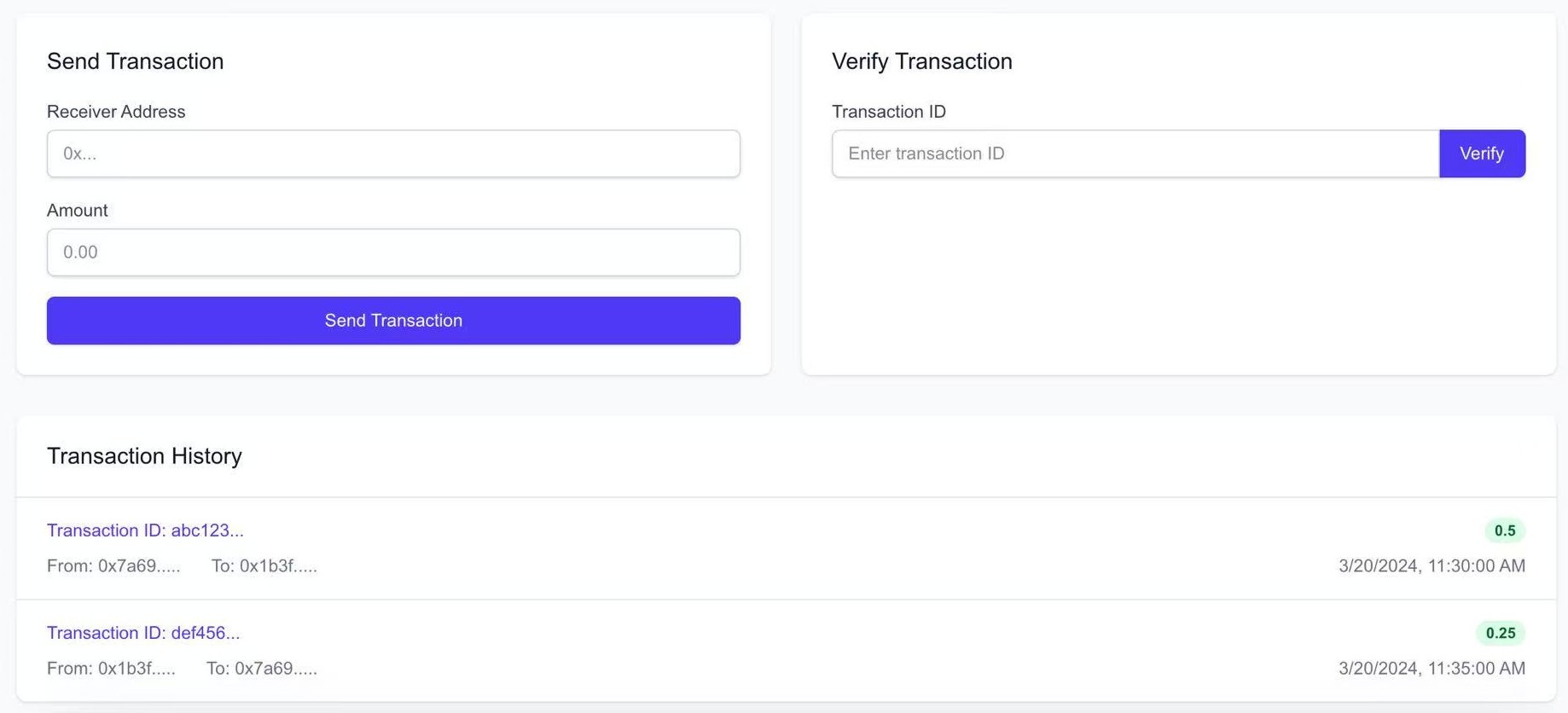
SPICE on FPGA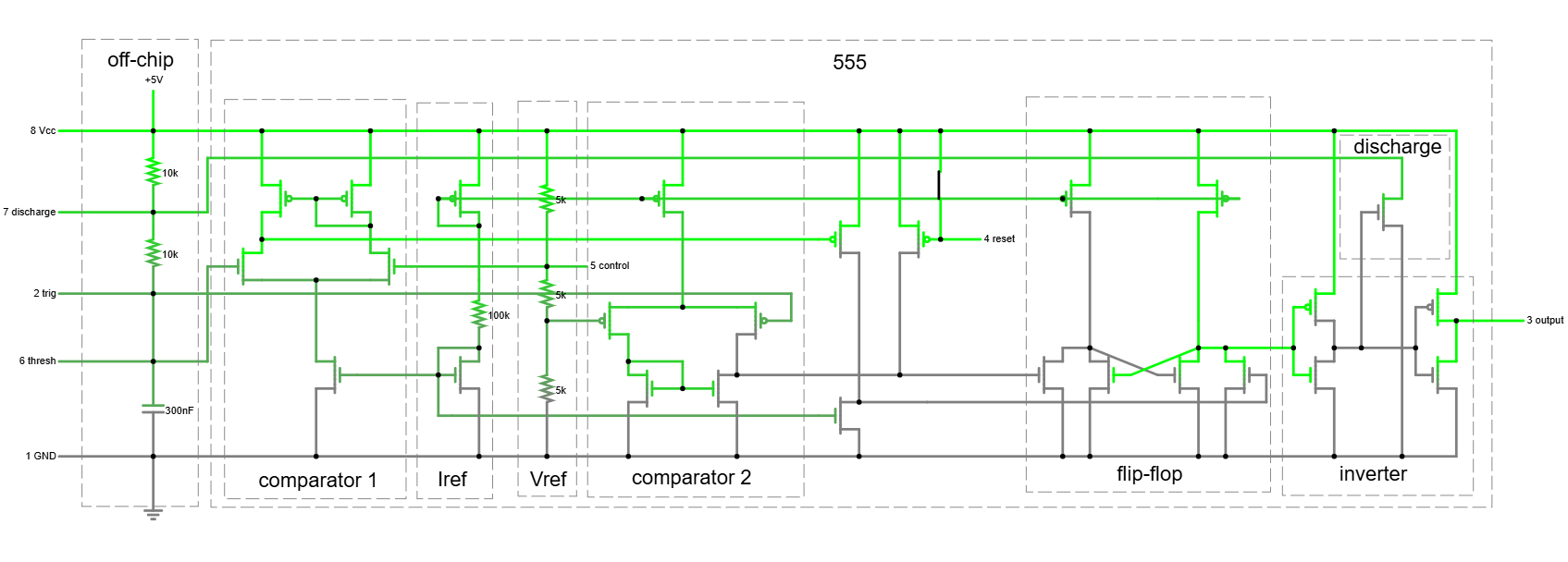
Final Project for ELEN 4824 Computer Architecture 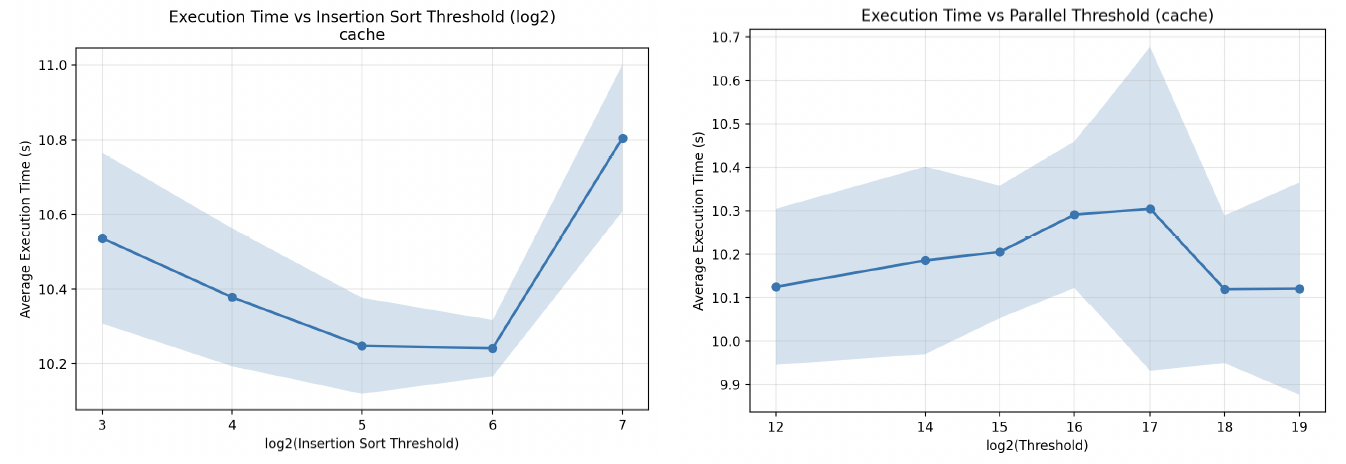
Final Project for ELEN 4312 Analog Electronic Circuits 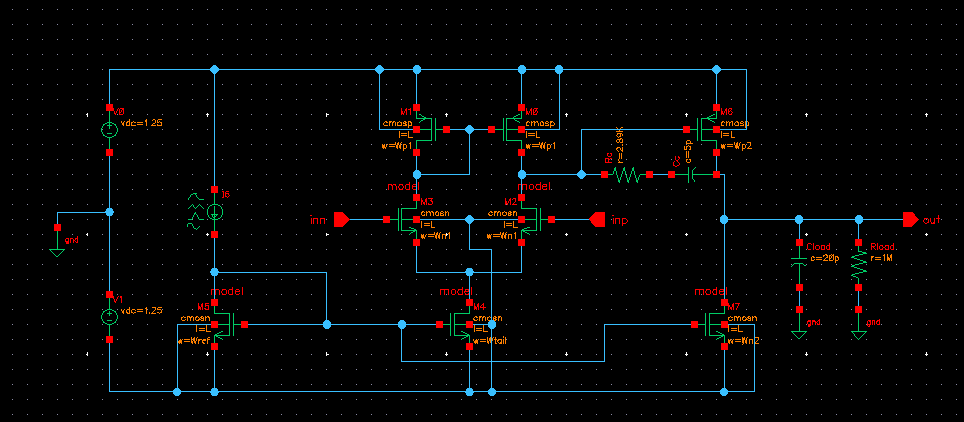
Final Project for CSEE 4823 Advanced Logic Design 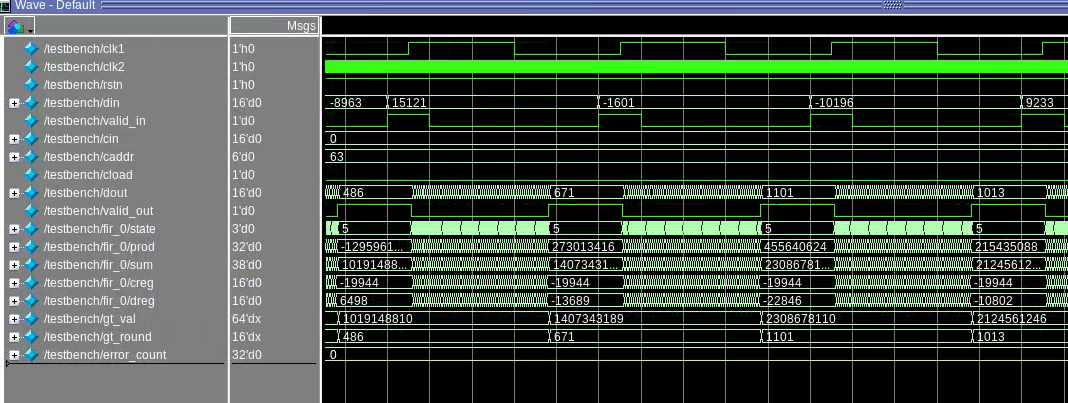
Final Project for EECS 4321 Digital VLSI Circuits 
2024
A new Gaussian Process-based modeling framework that predicts the physico-chemical properties of chemical species.
Recommended citation: Cao, X., Gong, M., Tula, A., Chen, X., Gani, R., & Venkatasubramanian, V. (2024). An improved machine learning model for pure component property estimation. Engineering, 39, 61–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2023.08.024
Download Paper
2024
SEDI Poster 2025
Recommended citation: Ming Gong, Michael I. Bergman, An experimental ultrasonic method to determine a scattering quality factor, with application to earth's inner core, Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2025, 107456, ISSN 0031-9201, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pepi.2025.107456.
Download Slides
2025
Identify optimal combination of loss function and data to create a model that can generates an automated tracing most consistent with the ground truth
2025
Accurate tracing of grain boundaries in microscopy images is vital in material science, yet current models need more data and a more accurate loss function. In this report, we present a twofold contribution to improving grain-tracing U-nets.
2025
An experimental study of the scattering of ultrasonic compressional waves in an hcp Zn-Sn alloy, serving as an analog to the Fe alloy in Earth’s inner core to better understand the origin of inner core seismic attenuation.
Recommended citation: Ming Gong, Michael I. Bergman, An experimental ultrasonic method to determine a scattering quality factor, with application to earth's inner core, Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 2025, 107456, ISSN 0031-9201, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pepi.2025.107456.
Download Paper | Download Slides
2025
Loose-fitting continuous ECG sensing T-shift using capacitive sensing
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown file that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown!
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field.
Class Tutor, Bard College at Simon's Rock, 2023
Class Tutor, Bard College at Simon's Rock, 2023
Class Tutor, Bard College at Simon's Rock, 2023
Class Tutor, Bard College at Simon's Rock, 2024
Class Tutor, Bard College at Simon's Rock, 2024
Class Tutor, Bard College at Simon's Rock, 2024
Head TA, Columbia University, 2025
TA, Columbia University, 2026