5 File IO
Published:
System calls
open()
int open(const char *path, int oflag, mode_t mode);
modefor file permission if new file created
/* Example file creation for writing ("w" for fopen())*/
#include <fcntl.h>
int fd;
mode_t mode = S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH; // rw- r-- r--
char *pathname = "/tmp/file";
// write only, create if not exist, replace if exist
fd = open(pathname, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, mode);
O_EXCL(exclusive): raise error ifO_CREATand file exists
creat(path, mode): open(path, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, mode)
int close(int fildes): Deletes the file descriptor table entry at fildes.
` off_t lseek(int fildes, off_t offset, int whence);` changes where next IO will take place.
- File offset stored in the file table entry for the current process
Read
ssize_t read(int fildes, void *buf, size_t nbyte);
Returns 0 on EOF and -1 on error.
- May block forever on “slow” read from pipes, FIFOs, sockets, or keyboard
- Disk IO is not “slow” read, since it eventually returns
Write
ssize_t write(int fildes, const void *buf, size_t nbyte);Also slow syscall for pipes, FIFOs, or sockets
- When reading side is too busy, pipe internal buffer fills up, and
write()blocks.
Atomicity: make sure either all/none are performed. Can’t only do a subset and fail in the middle
- E. appending to file:
lseek(); 2.write(), not atomic
write(O-APPEND)is atomicC stdio
wrapper on top of UNIX IO
FILE *fopen(const char *pathname, const char *mode); // open() int fclose(FILE *stream); // close() int fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int whence); // lseek() size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream); // read() size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream); // write()
Buffering
but maintain an internal buffer at application layer. Every operation may not translate to the kernel system call call. Can be buffered.
strace ./program # traces syscalls
File sharing
Kernel file data structure
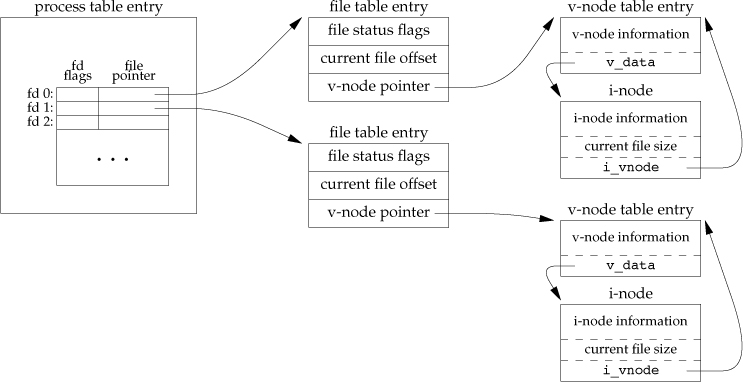
- Process table entry: array of file pointers, indexed by fd
- 0, 1, 2, are pre-opened by OS
- For two independent processes, they will have independent file table entries, but point to the same i-node
dup(fd)takes existing openfdand duplicates its process table entry. Both will point to the same file table entry.fork(), all descriptors are copied to the new process, as ifdup()ed. Parent and child share the same file table entry
- FIle table entry (possibly shared): instance of opened file
- When file opens, kernel prepares a structure i-node (v and i are combined to i-node for linux)
- 1-to-1 mapping between i-node entry and file
Open fork order
fork-then-open.c
if (fork() == 0)
sleep(1);
fd = open(path);
for (c = 'A'; c < 'A' + 5; c++) {
write(fd, &c, 1);
sleep(2);
}
Parent and child have their own file offset. Parent writes “a”, child writes “a” again on the same spot, overwrites it, only one copy written
- To coordinate, you’ll need to send a message to the other process, complicated
open-then-fork.c If open and fork order swapped, parent and child will share the same file table entry (offset), and “aa” will be printed.
